MAGAN
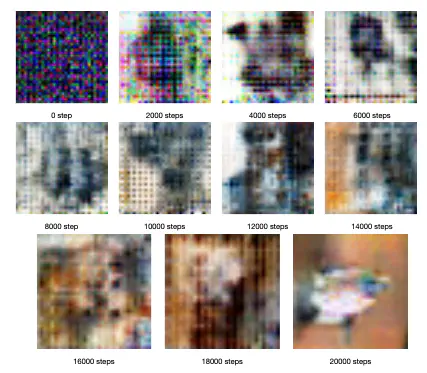
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) suffer from the instability of training because of Optimal Transportation (OT) problems. Based on Brenier’s Theorem, we converted OT problems into solving the elliptic Monge–Ampère Partial Differential Equation (MAPDE) by utilizing the finite difference method. In order to solve n (n > 3) dimensional MAPDE, we improved Neumann boundary conditions and extended a discretization of MAPDE for the numerical solution to enable the optimal map between generators and discriminators. The solution of MAPDE was regarded as a new divergence instead of Wasserstein Distance from WGAN.
We provided several computational examples to demonstrate that the precision was increased by 5.3%. Moreover, MAGAN was able to stabilize training with almost no hyperparameter tuning and the convergent speed of MAGAN was 317.2% faster than WGAN-GP on LSUN Bedrooms Database. MAGAN also achieved the Inception Score (IS) of 8.7 on CIFAR-10.